Diamonds come in a variety of colors. The majority of diamonds sold in the jewelry industry range from near colorless to very light yellow or brown. The most valuable are colorless diamonds (which have extraordinary ability to absorb all rays of light equally) and fancy colored diamonds (due to their rarity and uniqueness).
The color in Natural Fancy Colored Diamonds is present because of presence of certain elements like nitrogen, boron, etc. which were introduced in diamonds by nature during their formation in earth).
 Each colored diamond is different not only because of its natural body color but also because of the way it is shaped and finally polished. Most fancy color diamonds are cut into cushion or radiant shapes forms, which best bring out the depth of hue. The most skilled cutters shorten the optical light path through the diamond, creating the bright sparkle that is reflected from them. Cutting deeper pavilions and creating different facets may intensify color.
Each colored diamond is different not only because of its natural body color but also because of the way it is shaped and finally polished. Most fancy color diamonds are cut into cushion or radiant shapes forms, which best bring out the depth of hue. The most skilled cutters shorten the optical light path through the diamond, creating the bright sparkle that is reflected from them. Cutting deeper pavilions and creating different facets may intensify color.
 The cutting of colored diamonds is significantly important, performed by highly skilled craftsmen who combine their technical knowledge with a deep appreciation for beauty and color. Different regions of the earth have yielded particular types of colored diamonds, and each color requires a master cutter’s knowledge and appreciation to unlock the beauty within.
The cutting of colored diamonds is significantly important, performed by highly skilled craftsmen who combine their technical knowledge with a deep appreciation for beauty and color. Different regions of the earth have yielded particular types of colored diamonds, and each color requires a master cutter’s knowledge and appreciation to unlock the beauty within.
Color is the most important factor in determining the beauty and value of a gemstone. There are four main factors involved in a gemstone’s color: hue, tone, saturation, and distribution.
Hue is the term used for the actual color of the spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo or violet. The more pure a gemstone’s hue, the more valuable it is. Because gemstones are composed of many naturally occurring elements, they typically emit one dominant color and one or more underlying colors.
Tone represents how light or dark a stone appears depending on how much brown, black, gray or white is present.
Saturation is the intensity of brightness of the color. The more color saturated a gemstone is, the more valuable it becomes.
Distribution is how evenly the color spreads out across the body of the gemstone.
Rarity
No other jewel combines the rarity, beauty and sex appeal of a colored diamond. The majority of white diamonds are not rare. For over 60 years, the DeBeers cartel has convinced Americans that diamonds equate with love and to be treasured. However, colored diamonds are truly exceedingly rare and are simply geological flukes. For every 100,000 D-flawless diamonds, there is probably one colored diamond, and it is probably not flawless. The beauty and the rarity of these colored diamonds have spawned unprecedented desire and unparalleled prices.
Red diamonds are undoubtedly the rarest of colored diamonds. Green and Blue colored diamonds follow closely behind and are exceptionally rare. Following in rarity are the Purple, Pink and Violet colors. The next layer of rarity goes to orange and olive. Yellow, brown, champagne, gray and black diamonds are only modestly rare.
 Before the discovery of the Argyle mine in Western Australia in the mid-1980s, the finest quality pink diamonds found elsewhere were very faintly colored. Argyle pinks and purple-pinks in contrast, have a characteristic full-bodied, bright and intense color. “Of every 39.2 million carats of diamonds mined at the Argyle, only 40 carats of pink diamond is deemed worthy of being presented for sale at their annual, invitation-only tenders. This is rarity as defined by Mother Nature.
Before the discovery of the Argyle mine in Western Australia in the mid-1980s, the finest quality pink diamonds found elsewhere were very faintly colored. Argyle pinks and purple-pinks in contrast, have a characteristic full-bodied, bright and intense color. “Of every 39.2 million carats of diamonds mined at the Argyle, only 40 carats of pink diamond is deemed worthy of being presented for sale at their annual, invitation-only tenders. This is rarity as defined by Mother Nature.
Some of the rarest and most famous colored diamonds where brought together at the Smithsonian Museum in 2003, being part of an exhibit titled The Splendour of Diamonds (above photo). The exhibit lasted from June 27th to September 30th and featured a number of exceptional colored diamonds: (top row left to right) the Steinmetz Pink, the Millennium Star, the Allnatt Diamond (bottom row left to right) the Heart of Eternity, the Pumpkin Diamond, the T. Yellow, the Moussaieff Red and the Ocean Dream.
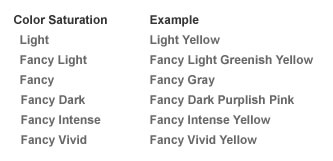
Color Saturation
Fancy Colored diamonds are graded according the saturation of the color along with different hues present in them. Following is a sample scale of color saturation:
In Fancy colored diamonds, main dominant color is listed after the modifying colors. If a diamond is graded as Fancy Grayish Greenish Yellow then the dominant color would be yellow with gray and green as modifying colors.
One important factor to remember is that in colored diamonds, clarity is secondary to the intensity of the diamond’s color.
Enhanced Color

Due to the rarity and high prices of naturally occurring colored diamonds, people were forced into finding a lower priced alternative. Scientist came up with a process which mimics the way diamonds are colored naturally. The most common process used in enhancing diamonds in the industry is called irradiation. This is a process in which natural diamonds with non fancy colors are subjected to high energy particles (alpha, beta, gamma, neutrons, x-rays or microwaves) in a properly equipped laboratory. Some of these diamonds are often subjected to further color enhancement by heating them at high temperatures of up to 1400 degree Celsius. The diamonds processed in this manner are called enhanced fancy colored diamonds and are completely safe to the wearer.
Most diamond colors can be artificially induced. Proof that a stone has a natural color can only be obtained from a gemological laboratory. When considering the purchase of an expensive stone, it is important to have a certificate from an independent laboratory stating the natural origin of its color. However, problems can occur: for instance, when testing green diamonds, it is difficult to differentiate a natural from an artificially-induced color. The process of artificially altering the color to green involves irradiating which can also occur naturally. Thus green stones, despite their rarity, are more difficult to sell unless indisputable proof of color origin can be found.